Abdominal Pain: Causes and Treatments
admin
- 0
The stomach, the seat of essential functions, can sometimes become the messenger of mysterious ailments. Abdominal pain is common, but its origin can vary greatly. Understanding its nature, duration and associated signals is crucial to assess the need for a medical consultation.
In this article, we will explore the many causes of abdominal pain, identify the warning signs, and most importantly, know when it is necessary to consult a healthcare professional. Distinguishing between temporary discomfort and serious problems helps avoid unexpected complications.
Need medical advice?
What is abdominal pain?
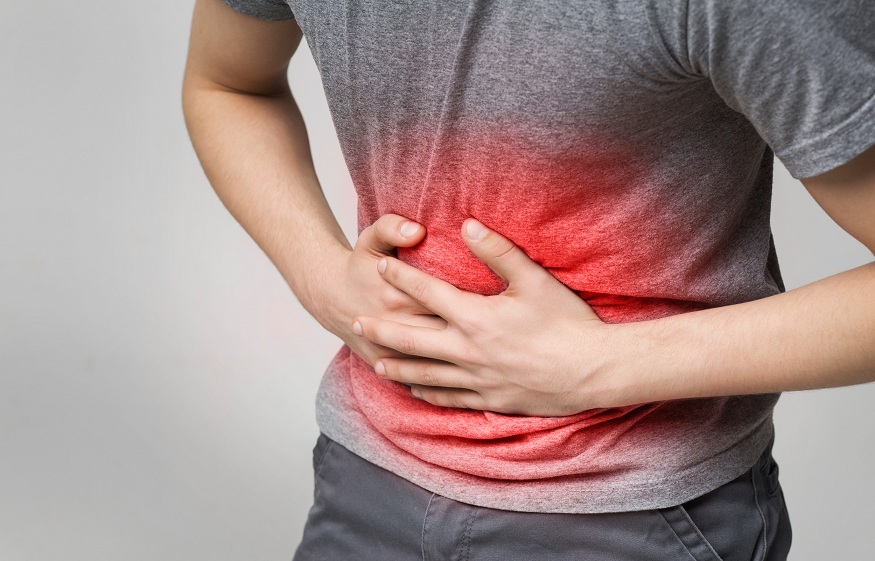
Abdominal pain refers to any feeling of discomfort, discomfort, or pain located in the belly area, also known as the abdomen. This anatomical area includes a multitude of vital organs such as the stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, and many others.
Abdominal pain can vary in intensity, duration, and character, ranging from a mild feeling of discomfort to a sharp, persistent ache.
Importance of Understanding Abdominal Pain
Understanding abdominal pain is crucial because it can be an early sign of underlying health problems . Recognizing the difference between minor pain and potentially serious pain can allow for early medical intervention, preventing potential complications.
What are the common causes of abdominal pain?
The causes of abdominal pain are diverse. They can result from:
Gastrointestinal problems : Disorders such as gastritis, ulcers, colitis and intestinal infections can cause abdominal pain.
Inflammation of the appendix : Appendicitis is a painful condition that requires surgery.
Digestive problems : Improper diet, indigestion or food intolerance can cause temporary abdominal pain.
Gallstones : Gallstones can cause severe pain, especially after meals .
Urinary Tract Infections : Urinary tract infections can cause pain in the lower abdomen .
Menstrual disorders : Abdominal pain may accompany menstruation in women .
Hernias : Hernias can cause abdominal pain when they become pinched or obstructed .
More serious medical conditions : Conditions such as intestinal obstruction, pancreatitis, kidney problems and other conditions require immediate medical attention.
Types of Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain can be classified into different types based on its character, duration, and location, which can help identify the underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment. Here are some common types of abdominal pain:
Acute vs. Chronic Pain
Acute Pain : This type of pain is sudden and severe, usually caused by conditions such as appendicitis, kidney stones, or intestinal obstruction. Acute pain may require immediate medical attention.
Chronic Pain : Chronic abdominal pain lasts for a long period of time, often weeks or months. It may be related to chronic medical conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, or long-term health problems.
Localized vs. generalized pain
Localized Pain : This pain is felt in a specific area of the abdomen. For example, pain due to appendicitis may be felt in the right lower quadrant.
Generalized Pain : Generalized abdominal pain spreads over a larger area of the abdomen. It may be a sign of infection, inflammation, or a condition affecting multiple organs.
Dull vs. sharp pains
Dull Abdominal Pain: Dull abdominal pain is often described as a feeling of pressure, discomfort or diffuse discomfort. It may be associated with minor digestive upsets or indigestion.
Acute Pain: Acute abdominal pain is felt as a sharp, intense, and often stabbing sensation. It can indicate problems such as serious infections, gallstones, or acute inflammation.
Causes of abdominal pain
Abdominal pain can often be attributed to various gastrointestinal disorders .
Gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammation of the stomach lining, usually caused by a bacterial infection, excessive use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or stressors. Abdominal pain related to gastritis is often described as a burning or discomforting sensation in the upper abdomen.
Ulcer
Peptic ulcers are open sores that form on the lining of the stomach or small intestine. They can cause abdominal pain, usually felt as a burning or stabbing pain in the upper abdomen, which may be worse after meals.
Constipation
Constipation occurs when stools are difficult to pass, which can cause abdominal pain and a feeling of bloating. Constipation pain is usually located in the lower abdomen.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Irritable bowel syndrome is a functional disorder of the digestive system that causes abdominal pain associated with changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea, constipation, or alternating between the two. Abdominal pain in IBS is often described as cramping or spasming.
Sigmoiditis and diverticulitis
Diverticulitis is an inflammation or infection of the diverticula, small pouches that can form on the inner wall of the colon. When this condition specifically affects the sigmoid portion of the colon, it is called sigmoiditis. The sigmoid colon is the part of the large intestine located just before the rectum.
Sigmoiditis :
This specific inflammation of the sigmoid portion of the colon can cause severe abdominal pain, usually located in the lower left quadrant of the abdomen. Other symptoms may include fever, chills, constipation, or, conversely, diarrhea. As mentioned earlier, sigmoiditis is a specific form of diverticulitis.
Diverticulitis :
The presence of diverticula is relatively common, especially in older adults, and the condition is called diverticulosis. However, when these diverticula become inflamed or infected, it is called diverticulitis. In addition to pain, it can manifest itself with nausea, vomiting, abdominal tenderness, distension, or even blood in the stool. Diverticulitis can be due to perforation of the diverticula, obstruction, or infection. Risk factors include older age, eating a low-fiber diet, and being sedentary.
Infections
Bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections of the stomach, intestines, or other abdominal organs can cause abdominal pain, often accompanied by symptoms such as fever, nausea, and diarrhea .
Gynecological conditions
Problems specific to the female reproductive organs, such as ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, pelvic infections, or endometriosis , can cause abdominal pain in women.
Urinary disorders
Urinary tract infections , kidney stones, or other kidney and bladder problems can cause pain in the lower abdominal area.


